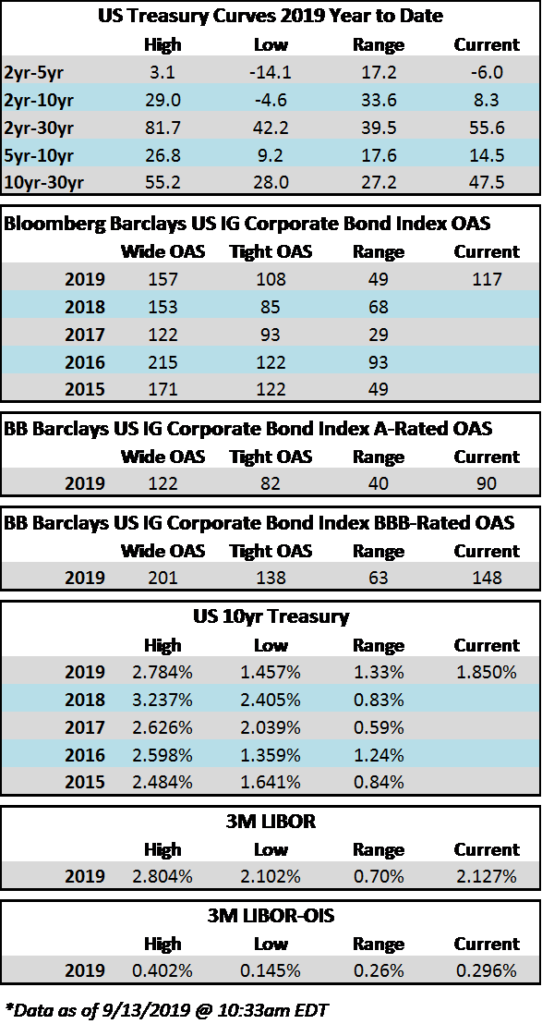
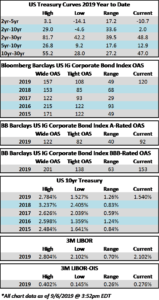
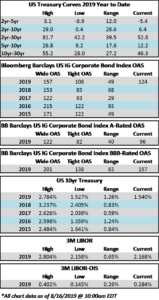
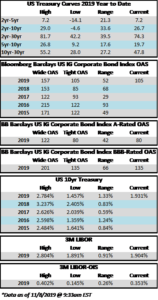
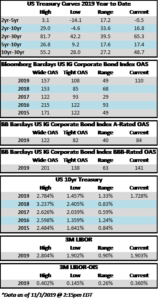
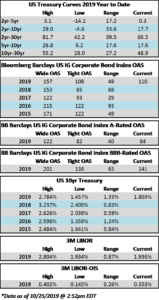
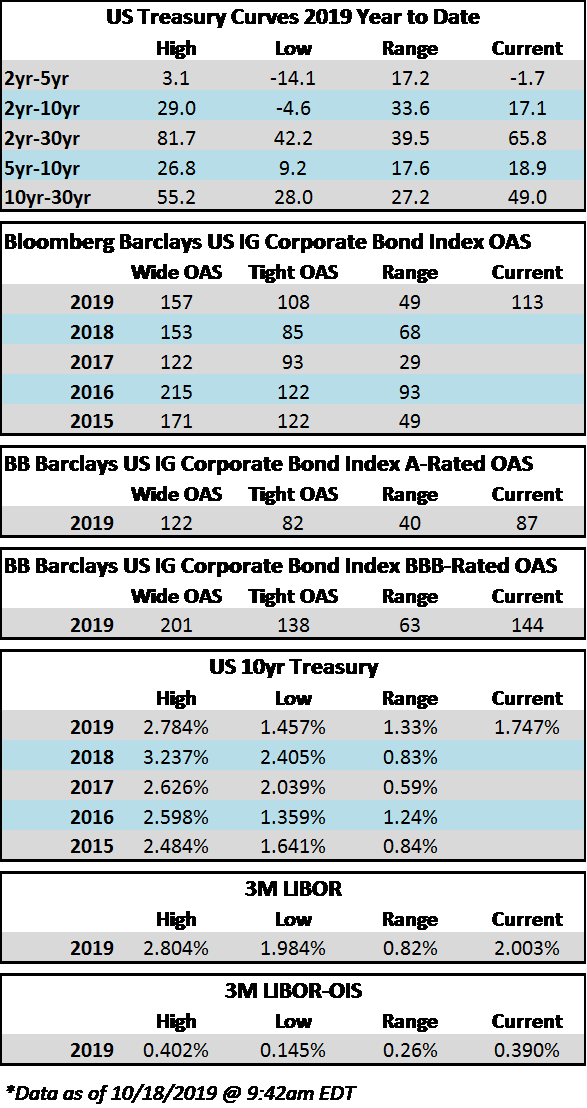
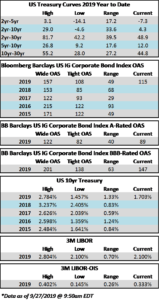
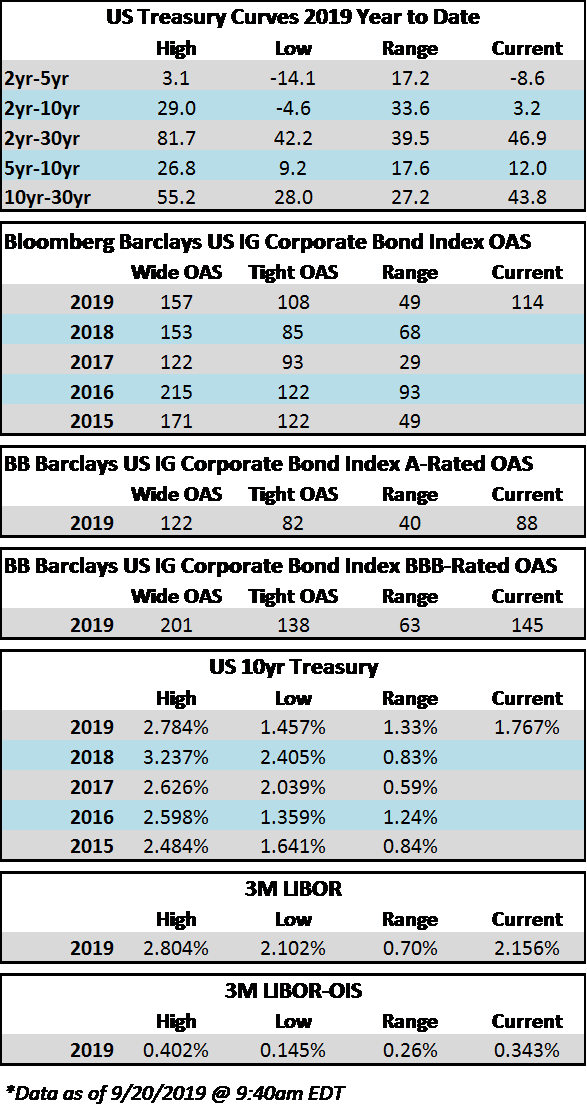
Credit spreads are set to finish the week generally unchanged but may be a touch wider in some spots when it is all said and done. The spread on the Bloomberg Barclays Corporate Index opened the holiday shortened week at 105 and closed at 106 on Thursday. There is positive sentiment in the markets on Friday morning amid China-US trade innuendo out of Washington. For the second week in a row we have seen a relatively significant move in treasuries; last week it was higher rates and this week lower. The 10yr Treasury closed the prior week at 1.94% and is now 1.83%, 11 basis points lower on the week as we go to print.
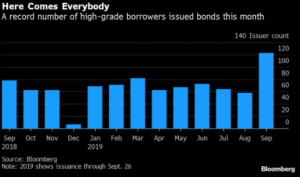
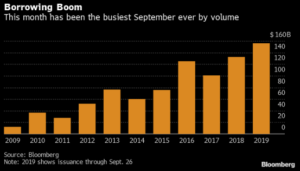
The primary market posted an impressive haul this week, especially considering the fact that the market was closed on Monday. It was the second largest volume week of the year thanks to a big boost from AbbVie, which printed a $30bln deal that featured 10 different maturities. With one deal pending this morning, weekly issuance will come in at the $50bln mark. Oddly enough both the largest and second largest issuance weeks in 2019 have both come on holiday shortened weeks. The largest volume week was the week of Labor Day when nearly $75bln of new debt was priced in just four days. According to data compiled by Bloomberg, 2019 issuance stands at $1,065bln which trails 2018 by -4.4%.
According to Wells Fargo, IG fund flows during the week of November 7-November 13 were +$2.8bln. This brings YTD IG fund flows to +$252bln. 2019 flows are up 9.5% relative to 2018.
Bloomberg) AbbVie Propels High-Grade Issuance to Year’s Second-Biggest Week
- It’s the second-biggest week of the year for U.S. investment-grade issuance, which at about $50 billion in volume trails only the record-setting start to September.
- AbbVie’s $30 billion deal on Tuesday clocked in as the year’s largest bond sale and the fourth-biggest ever, helping to establish this week’s second-place finish
- Supply for the week stands at $49.4 billion as of Thursday with more deals potentially coming Friday given a shorter window to sell debt after Monday’s Veteran Day close
- The first week of September saw $75 billion of high-grade bond sales, the most for any comparable period since records began in 1972
- This week overtook the five days to May 9, when IBM and Bristol Myers brought $39 billion in acquisition-related supply in a 24-hour span
- AbbVie’s $30 billion deal on Tuesday clocked in as the year’s largest bond sale and the fourth-biggest ever, helping to establish this week’s second-place finish
(Bloomberg) Here’s How KKR Might Just Pull Off the Biggest LBO in History
- One of the private equity industry’s titans called it a “stretch,” and it’s been dismissed as a pipe dream by a bevy of analysts.
- Yet interviews in recent days with debt-market specialists suggest that KKR & Co. could find a narrow path to finance what would be the biggest leveraged buyout in history: a potential take-private deal for pharmacy chain Walgreens Boots Alliance Inc. that analysts have estimated would need to be funded with at least $50 billion of debt.
- The challenge for any Walgreens suitor will be raising the necessary money via the markets of choice for private equity firms — junk-rated loans and bonds — which have become fragile after an unprecedented borrowing binge left investors with a hangover. Debt funds that financed more than $3.5 trillion of leveraged buyouts in the past decade have become pickier, leaving banks stuck holding more than $2 billion of unsold loans on their balance sheets as recently as last month.
- But a road map may be hidden in two other recent debt-fueled takeovers: Dell Technologies Inc.’s $67 billion takeover of EMC Corp. in 2016 and Charter Communications Inc.’s $78.7 billion acquisition of Time Warner Cable Inc. that same year.
- Junk-rated Dell and Charter both borrowed heavily in the investment-grade bond market by issuing secured debt. T-Mobile US Inc. is going down a similar route to help pay for its purchase of Sprint Corp.
- In Charter’s case, it pledged security to new and existing bonds issued by higher-rated Time Warner to ensure the debt remained investment-grade. Dell used a similar strategy when it bought investment-grade rated EMC. Walgreens’s debt could be segregated into two borrowing structures at a holding company level and an operating company portion, with investment-grade debt placed on the latter.
- In doing so, Dell and Charter won access to the most stable part of the corporate debt market, where investors are still buying heavily as an alternative to low or negative-yielding assets elsewhere. At the same time, they limited their reliance on leveraged finance markets, where sentiment can shift quickly and prove costly.
- Both companies did tap those markets, but with more manageable offerings. Bankers who asked not to be identified estimated that Walgreens would be able to raise between $10 billion and $20 billion of junk-rated debt to fund a buyout.
- Other market participants, who asked not to be named because they weren’t authorized to speak publicly, said KKR still might need to find a deep-pocketed third-party investor to help put more equity into the deal.
- Or it may seek to spin off a portion of Walgreens to lessen its financing needs. The company’s European operations could potentially bring in $18 billion to $20 billion, CreditSights analyst James Goldstein said in a phone interview.
 (Bloomberg) The Repo Market’s a Mess. (What’s the Repo Market?): QuickTake
(Bloomberg) The Repo Market’s a Mess. (What’s the Repo Market?): QuickTake