CAM High Yield Weekly Insights
Fund Flows & Issuance: According to a Wells Fargo report, flows week to date were -$0.6 billion and year to date flows stand at -$47.5 billion. New issuance for the week was nil and year to date issuance is at $101.2 billion.
(Bloomberg) High Yield Market Highlights
- U.S. junk bonds are poised to gain for the fourth straight week, the longest winning streak since mid-August, with yields tumbling to mid-September lows after Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell signaled on Wednesday that the central bank will likely slow the pace of interest-rate increases. The biggest gains came on Thursday, when the market saw its best advance in more than three weeks after the Fed’s favored inflation gauge posted a smaller-than-expected monthly advance and data showed a cooling in the manufacturing sector.
- The inflation measure, the personal consumption expenditures index, rose 0.3% in October, less than the 0.4% forecast by economists.
- The rally that followed the release Thursday drove the junk-bond market to a weekly gain of 0.88% and pushed yields down to 8.43%, a more than 11-week low.
- The gains spanned across ratings. CCC yields fell significantly below 14% to close at 13.83%, a more than 11-week low.
- CCCs are also headed for the fourth straight week of gains, with week-to-date returns of 0.73%. The 0.99% gains on Thursday were the biggest one-day rally in three weeks.
- The recent rally in the junk bond market was also partly fueled by lack of supply. The primary market is expected to largely remain quiet as banks work out of the losses from this year’s leveraged buyout debt.
- October was the slowest month for new bond sales since 2008, with a mere $3.7b. November ground to a halt after a promising start to end with a modest $9b, the slowest for that month since 2018.
- Year-to-date supply at $95b has also been the lightest in 14 years.
- Junk bonds are losing steam early Friday post stronger than expected employment data.
(Bloomberg) Powell Signals Downshift Likely Next Month, More Hikes to Come
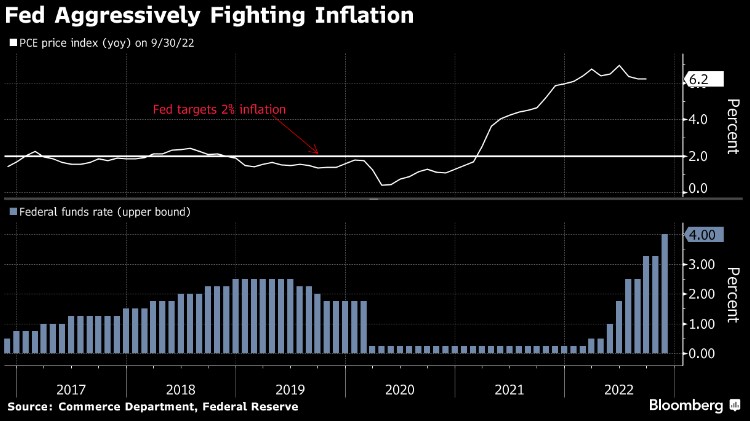
- Chair Jerome Powell signaled the Federal Reserve will slow the pace of interest-rate increases next month, while stressing borrowing costs will need to keep rising and remain restrictive for some time to beat inflation.
- His comments, in a speech Wednesday at the Brookings Institution in Washington, likely cement expectations for the Fed to raise interest rates by 50 basis points when they meet Dec. 13-14, following four straight 75 basis-point moves.
- “The time for moderating the pace of rate increases may come as soon as the December meeting,” Powell said in the text of his speech. “Given our progress in tightening policy, the timing of that moderation is far less significant than the questions of how much further we will need to raise rates to control inflation, and the length of time it will be necessary to hold policy at a restrictive level.”
- The Fed’s actions — the most aggressive since the 1980s — have lifted the target range of their benchmark rate to 3.75% to 4% from nearly zero in March. Powell said rates are likely to reach a “somewhat higher” level than officials estimated in September, when the median projection was for 4.6% next year. Those projections will be updated at the December meeting.
- Investors see the Fed pausing hikes in the second quarter once rates reach about 5%, according to pricing in futures contracts.
- Powell said the central bank is forecasting 12-month inflation based on its preferred gauge, the personal consumption expenditures price index, of 6% through October, and a 5% core rate.
- There hasn’t been enough strong evidence to make a convincing case that inflation will soon decelerate, he said.
- “It will take substantially more evidence to give comfort that inflation is actually declining,” he said. “The truth is that the path ahead for inflation remains highly uncertain.”
- He added that “despite the tighter policy and slower growth over the past year, we have not seen clear progress on slowing inflation.”
- Powell launched into a discussion of service costs, focusing on scarce supply in the labor market, with the gap in labor-force participation mostly explained by pandemic-era retirements in his view.
- “These excess retirements might now account for more than 2 million of the 3 1/2 million shortfall in the labor force,” he said.
- He said the labor market is only showing “tentative signs” of what he called “rebalancing,” while wages are “well above” levels consistent with 2% inflation over time.
This information is intended solely to report on investment strategies identified by Cincinnati Asset Management. Opinions and estimates offered constitute our judgment and are subject to change without notice, as are statements of financial market trends, which are based on current market conditions. This material is not intended as an offer or solicitation to buy, hold or sell any financial instrument. Fixed income securities may be sensitive to prevailing interest rates. When rates rise the value generally declines. Past performance is not a guarantee of future results.